Caffeine is a popular stimulant. Many rely on it for a quick energy boost.
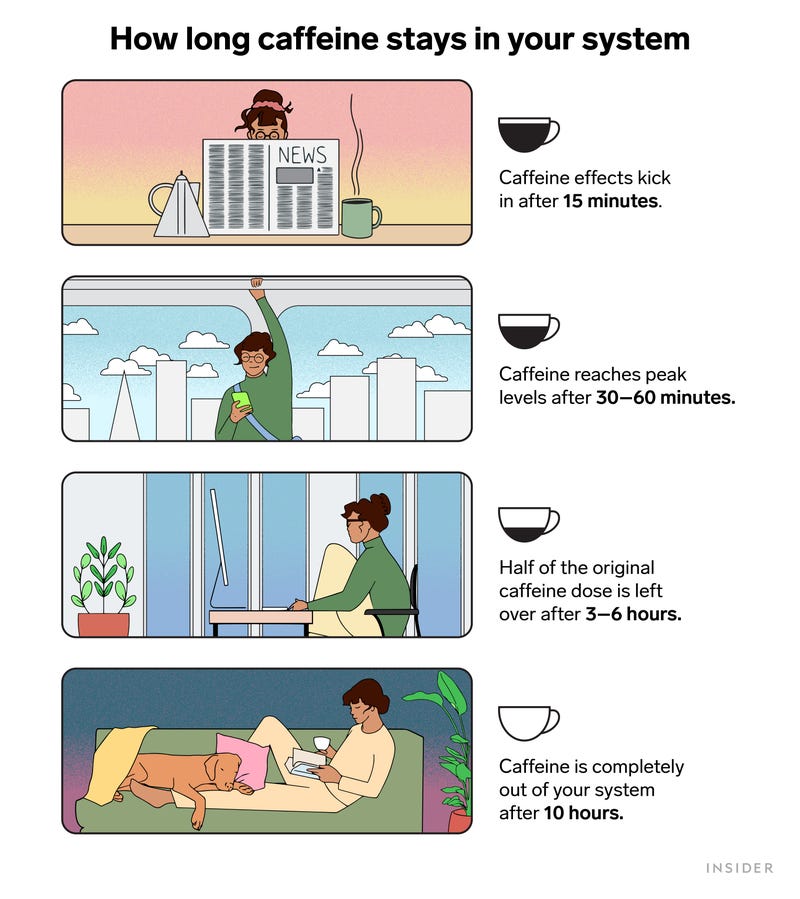
So, how long does it take for caffeine to kick in? Typically, you may start feeling its effects within 15 to 45 minutes. Caffeine works by blocking adenosine, a chemical that makes you feel tired. This process gives you a burst of energy and alertness.
But the speed at which caffeine kicks in can vary. Factors like your metabolism, body weight, and tolerance play a role. Some may feel the jolt almost instantly, while others might wait a bit longer. Understanding how caffeine works can help you make the most of your coffee, tea, or energy drink. Ready to dive deeper? Let’s explore the science behind caffeine’s effects.

Credit: greenssteel.co.uk
Caffeine Absorption
Caffeine is a popular stimulant found in coffee, tea, and energy drinks. Many people rely on it to stay alert and focused. Understanding how caffeine absorption works can help you make the most of its benefits.
How The Body Processes Caffeine
Once you consume caffeine, it quickly enters your bloodstream. The stomach and small intestine absorb it. This process takes about 45 minutes. The liver then metabolizes caffeine. It breaks it down into different compounds. These compounds affect the brain and body.
Factors Affecting Absorption Rate
Several factors influence how fast caffeine kicks in. Your age, weight, and metabolism play a role. Younger people and those with a faster metabolism absorb it quicker. Food in your stomach can slow down absorption. Drinking caffeine on an empty stomach speeds it up. Medications and hormonal levels also impact the rate. Pregnant women and those on birth control pills may process caffeine slower.
Time To Feel Effects
Caffeine is known for its quick energy boost. But how long does it take to feel the effects? Understanding the timeline helps you plan your caffeine intake better. Let’s dive into the details.
Typical Onset Time
The typical onset time for caffeine to kick in ranges between 15 to 45 minutes. After you consume caffeine, it quickly enters your bloodstream. You might start feeling more alert and awake within this window.
The exact time can vary based on several factors. These include the type of caffeine you consume and your body’s metabolism rate.
Variations Among Individuals
Individual variations play a significant role in how quickly you feel the effects of caffeine. Some people might feel it within 15 minutes, while others might take longer.
Factors that influence this include:
- Age: Younger people tend to metabolize caffeine faster.
- Body weight: Heavier individuals might take longer to feel the effects.
- Genetic factors: Your genes can affect how your body processes caffeine.
- Tolerance level: Regular caffeine users might need more time to feel the effects.
| Factor | Impact on Onset Time |
|---|---|
| Age | Younger = Faster |
| Body Weight | Heavier = Slower |
| Genetic Factors | Varies |
| Tolerance Level | Higher Tolerance = Slower |
Understanding these factors helps you gauge when you’ll feel that caffeine boost. It can also help you avoid overconsumption and its side effects.
Caffeine Sources
Caffeine is a popular stimulant found in many foods and drinks. It helps people stay alert and awake. Different sources provide varying amounts of caffeine. Understanding these sources can help manage your caffeine intake.
Common Beverages
Coffee is one of the most common sources of caffeine. A standard cup contains around 95 mg of caffeine. Espresso has more caffeine per ounce, about 63 mg. Tea is another popular choice. Black tea contains around 47 mg per cup, while green tea has about 28 mg. Soft drinks also contain caffeine. A can of cola has about 34 mg. Energy drinks are stronger, often containing 70 to 100 mg per serving.
Alternative Sources
Chocolate contains caffeine, too. Dark chocolate has around 20 mg per ounce. Milk chocolate has less, about 6 mg per ounce. Some over-the-counter pain relievers include caffeine. These can have up to 65 mg per tablet. Caffeine pills are a direct source. They usually contain 100 to 200 mg per pill. Certain foods and snacks are also caffeinated. These can range from 10 to 50 mg per serving.
Impact On The Brain
Caffeine is a common stimulant found in coffee, tea, and energy drinks. It has a significant impact on the brain, affecting various functions and processes. Understanding how caffeine works can help you make informed choices about your consumption.
Stimulant Effects
Caffeine acts as a stimulant on the brain. It boosts alertness and reduces fatigue. This happens because caffeine blocks the effects of adenosine, a chemical that promotes sleep.
When adenosine is blocked, dopamine and norepinephrine levels increase. This leads to heightened arousal, energy, and focus. The effects can be felt within 15 to 45 minutes after consumption.
Neurotransmitter Interaction
Neurotransmitters are chemicals that transmit signals in the brain. Caffeine influences the release and activity of several neurotransmitters.
| Neurotransmitter | Effect of Caffeine |
|---|---|
| Dopamine | Increases pleasure and alertness |
| Norepinephrine | Boosts energy and focus |
| Serotonin | Enhances mood and well-being |
The interaction with these neurotransmitters creates a sense of heightened alertness and well-being. This is why many people start their day with a cup of coffee.
Understanding the impact on the brain helps you use caffeine effectively. This knowledge can optimize your daily routine and improve your productivity.
Duration Of Effects
The duration of caffeine effects varies by individual. Factors include age, weight, and metabolism. Understanding these effects helps in timing caffeine intake for optimal benefits.
Peak Concentration
After consuming caffeine, it takes about 30 to 60 minutes to reach peak concentration in the bloodstream. During this time, you may start to feel more alert and awake. The exact time can vary based on individual differences and the form of caffeine consumed.
How Long It Lasts
The effects of caffeine can last anywhere from 3 to 5 hours. For some, it may extend up to 7 hours. This duration is affected by how quickly your body metabolizes caffeine. Below is a table that summarizes the typical duration:
| Factor | Duration |
|---|---|
| Average Duration | 3 to 5 hours |
| Extended Duration | Up to 7 hours |
Understanding how long caffeine lasts in your system can help manage intake. Avoid late-day consumption to prevent sleep disturbances.

Credit: www.homegrounds.co
Tolerance And Sensitivity
Many people wonder how long it takes for caffeine to kick in. The answer varies due to several factors. Two of the most significant factors are tolerance and sensitivity. These factors influence how your body reacts to caffeine. Let’s dive deeper into these aspects.
Building Tolerance
Regular caffeine consumption leads to tolerance. Tolerance means your body gets used to caffeine. Over time, you may need more caffeine for the same effect. This is common among regular coffee drinkers. The more you consume, the less impact it has. Your body adapts to the caffeine intake. This process can take a few weeks or months.
Building tolerance depends on your habits. Drinking several cups of coffee each day will build tolerance quickly. Occasional drinkers may not build tolerance as fast. Everyone’s body is different. Thus, your caffeine tolerance will vary from others.
Individual Sensitivity
Sensitivity to caffeine varies among individuals. Some people feel effects after a small amount. Others need larger doses. Genetics play a role in this. Your body’s ability to process caffeine affects your sensitivity.
Some people have a fast metabolism. They process caffeine quickly. For them, the effects wear off sooner. Others have a slow metabolism. They may feel the effects for longer periods. Age, weight, and health also influence sensitivity. Knowing your sensitivity helps manage your caffeine intake better.
Health Considerations
Caffeine provides a quick energy boost. But it’s important to consider health aspects. Understanding safe consumption levels and possible side effects is crucial. This ensures you enjoy the benefits without harming your health.
Safe Consumption Levels
The FDA suggests that up to 400 milligrams of caffeine per day is safe for most adults. This equals about four 8-ounce cups of coffee. Pregnant women should limit intake to 200 milligrams daily. This is about two 8-ounce cups of coffee. Children and teens should consume less caffeine. Their growing bodies are more sensitive to its effects.
| Group | Safe Daily Limit |
|---|---|
| Adults | 400 mg (4 cups of coffee) |
| Pregnant Women | 200 mg (2 cups of coffee) |
| Children and Teens | Less than adults |
Potential Side Effects
Overconsumption of caffeine can cause side effects. These include:
- Insomnia: Difficulty falling or staying asleep.
- Jitters: Feeling restless or anxious.
- Rapid Heartbeat: Increased heart rate.
- Digestive Issues: Stomach pain or nausea.
- Headaches: Pain in the head or neck area.
It’s essential to monitor your caffeine intake. Too much can harm your health. Balance is key to enjoying caffeine safely.
Maximizing Benefits
Maximizing the benefits of caffeine requires understanding its timing and interaction with other nutrients. Knowing when and how to consume caffeine can enhance its positive effects, such as increased alertness and energy. By optimizing your caffeine intake, you can make the most of your daily routine.
Optimal Timing
To get the most from caffeine, consider the timing of your intake. Caffeine begins to work within 15 minutes of consumption. It peaks in your bloodstream within 30 to 60 minutes. For a morning boost, drink coffee shortly after waking up. This helps combat morning grogginess. If you need an afternoon lift, have a cup of coffee or tea around 1-2 PM. Avoid late afternoon or evening caffeine to prevent sleep issues.
Combining With Other Nutrients
Caffeine’s effects can be enhanced by pairing it with the right nutrients. Consuming it with carbohydrates helps maintain energy levels. A small snack like a banana or a piece of toast can do the trick. Protein can also work well with caffeine. A protein-rich breakfast with your coffee can sustain energy longer. Hydration is crucial too. Drink plenty of water to support caffeine’s benefits and avoid dehydration.

Credit: www.onepeloton.com
Frequently Asked Questions
How Quickly Does Caffeine Start To Work?
Caffeine usually starts working within 15 to 20 minutes after consumption. It peaks in your bloodstream within 30 to 60 minutes.
What Factors Affect Caffeine Kick-in Time?
Factors like metabolism, age, weight, and tolerance influence how quickly caffeine kicks in. Individual sensitivity also plays a role.
Does Caffeine Affect Everyone The Same Way?
No, caffeine affects people differently. Some may feel energized quickly, while others might take longer or feel minimal effects.
How Long Does Caffeine Stay In Your System?
Caffeine has a half-life of about 3 to 5 hours. It can stay in your system for up to 10 hours.
Conclusion
Understanding caffeine’s effects helps manage energy and alertness. Generally, caffeine kicks in within 15 to 45 minutes. Individual factors, like age and metabolism, impact this timing. Knowing your body’s response can guide your caffeine intake. Pay attention to how you feel.
Adjust your consumption for optimal benefits. Stay informed, listen to your body, and enjoy your favorite caffeinated drinks responsibly.